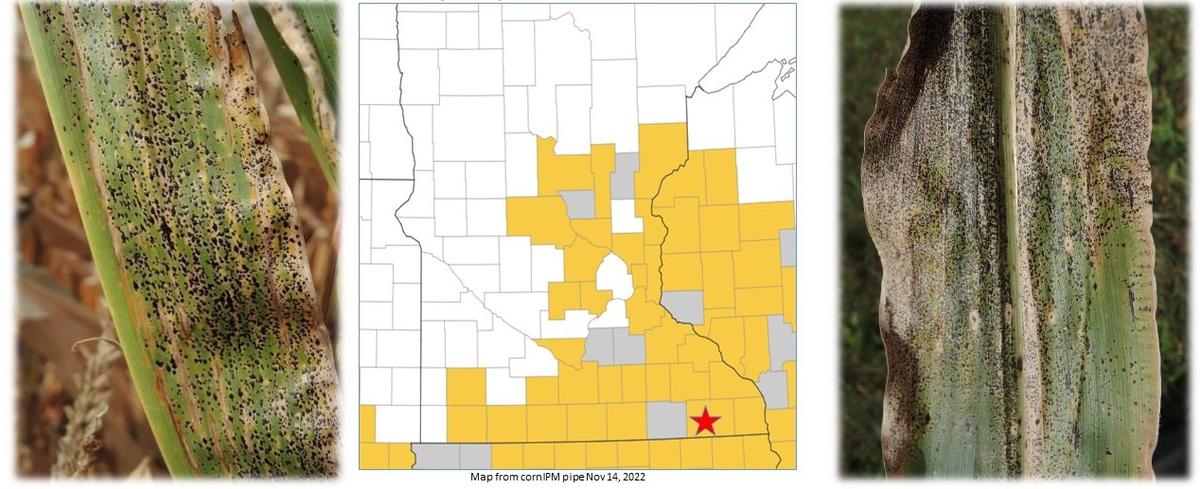
Typical symptoms of corn tar spot and a map of known distribution in Minnesota as of July 2023. Images were provided by the project team.
Background
Corn tar spot is a leaf disease caused by the fungus Phyllachora maydis. It produces black spots on leaves, and can cause significant yield loss for corn, the most widely grown crop in Minnesota. Yield loss can exceed 40%.
It was first detected in the United States in 2015 in Illinois and Indiana, and has since spread to multiple states in the Midwest, including southeastern Minnesota where it has been confirmed in 12 counties. There has been limited information about the distribution, biology, and management of corn tar spot.
Research questions
- What is the distribution of corn tar spot, and how established is it?
- How do we detect corn tar spot?
- How will corn tar spot respond to future weather conditions?
- What are our management options for corn tar spot, and how effective are they?
Outcomes
This project team made significant progress in developing knowledge and tools for the research and management of corn tar spot. They identified the pathogen in an additional 25 Minnesota counties, confirming that it is continuing to spread.
In collaboration with other colleagues, the MITPPC team created a DNA-based test to accurately detect corn tar spot. In addition, they developed a way to reliably inoculate corn with the pathogen in greenhouse settings, enabling future research on biology and management. This had not yet been accomplished by any other researchers.
The team wrote a diagnostics and methods guide on corn tar spot, the first of its kind. The guide helps to identify the pathogen and distinguish it from lookalikes, and describes its host range and distribution. This contributes to the greater body of research and provides critical information to growers.
This line of research continues in a separate project: Understanding key factors contributing to the spread and development of tar spot of corn caused by Phyllachora maydis in Minnesota.
Publications
- Development of a qPCR assay for species-specific detection of the tar spot pathogen Phyllachora maydis (PhytoFrontiers, 2023)
- A new and effective method to induce infection of Phyllachora maydis into corn for tar spot studies in controlled environments (Plant Methods, 2023)
- Tar Spot of Corn: A Diagnostic and Methods Guide (Plant Health Progress, 2023)
Outreach
- Extension education programs in Rosemount, Lamberton, Wilmar, Waseca, Morris, Pine City, Hutchinson, Cold Spring, Rochester, Faribault, Minneapolis, Little Falls, and Bloomington, MN and Grand Forks, ND, 2023
- “Strategic Farming” webinar for UMN Extension, 2023
- National Corn Disease meetings, 2023
- Meetings with regional and national researchers and agronomists with Bayer
- Crop Science and UMN Extension Educators, 2023
- Plant Pathology Seminar at The Ohio State University, 2023
- Contributor to Minnesota Crop News, University of Minnesota Extension
News and media
- Bursting the fungal menace of corn tar spot wide open (MITPPC, 2023)
- Researchers develop new corn tar spot diagnostics guide (MITPPC, 2023)
- Strategic Farming: Let’s talk tar spot of corn (Morrison County Record, 2023)
- Strategic Farming: Let's talk crops focused on tar spot of corn (Minnesota Crop News, UMN Extension, 2023)
- Corn tar spot showed up in Stearns County in 2022 (Minnesota Farm Guide, 2023)
- Beware: Mysterious fungus pathogens are among us: Diseases impact corn and soybean production in Minnesota (College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resources News, 2023)
- University of Minnesota Extension urges growers to scout for tar spot in corn (Southern Minn Faribault News, 2022)
- Strategic Farming: Field Notes focused on tar spot (Minnesota Crop News, UMN Extension, 2022)
- Corn tar spot reported in southeastern Minnesota (Minnesota Crop News, UMN Extension, 2022)
- Scout for tar spot of corn (Minnesota Crop News, UMN Extension, 2022)
- Tracking Tar Spot: Protecting Minnesota's corn (MITPPC)